When building a network, we sometimes face the situation of mixing industrial switches with ordinary routers. This hybrid application is more common in certain scenarios, such as connecting to office networks in industrial environments, or small businesses wanting to use existing ordinary routers to build simple industrial network monitoring. But before performing this operation, we need to understand some key points.

1、 The difference between industrial switches and ordinary routers
(1) Functional focus
Industrial switches are mainly used in the field of industrial automation, such as factory workshop equipment networking, smart grid equipment connection, and other scenarios. It needs to ensure the stability and reliability of data transmission in industrial production, and be able to adapt to harsh industrial environments. Ordinary routers are more used for home or office networks, mainly to connect different networks, such as connecting the home network to the Internet, so that multiple devices can share the network.
(2) Technical indicators
Bandwidth: Industrial switch bandwidth typically ranges from 1Gbps to 10Gbps or even higher. For example, common industrial grade 100Mbps switches have port speeds of up to 100Mbps, Gigabit switches have port speeds of up to 1000Mbps, and 10G switches can achieve 10Gbps. However, ordinary routers for home use typically have speeds ranging from 100Mbps to 1000Mbps. Common 100Mbps routers have WAN and LAN ports with speeds of 100Mbps, while gigabit routers have speeds of 1000Mbps. In industrial environments, if there are a large number of devices transmitting data simultaneously, such as frequent data exchange between automated production line equipment, high bandwidth industrial switches are needed to ensure smooth data transmission.
Protection level: Industrial switches have a higher protection level, such as commonly reaching IP30 or above. IP30 means it can protect objects with a diameter greater than 2.5mm from intrusion, prevent dust, and some industrial switches can even reach IP67, completely preventing dust intrusion, and can work normally even when submerged in water for a certain period of time. Ordinary routers generally do not have special protection levels and are mainly suitable for indoor ordinary environments. An environment like a factory workshop with a lot of dust and possibly slight water mist makes it difficult for ordinary routers to adapt.
Working temperature range: Industrial switches have a wide working temperature range, generally able to operate normally between -40 ℃ and 75 ℃. The working temperature range of ordinary routers is relatively narrow, usually around 0 ℃ to 40 ℃. In high-temperature workshops of steel plants or outdoor industrial equipment networking scenarios with cold winters in the north, ordinary routers cannot work properly, while industrial switches can operate stably.
Power supply: Industrial switches have various power supplies, including DC 24V, 48V, and some also support AC 220V. For example, some industrial environments use DC 24V power supply, and industrial switches can be adapted. Ordinary routers generally use AC 220V mains power. If there is only DC power supply in an industrial environment, ordinary routers cannot be used.
Port type: In addition to common Ethernet ports, industrial switches may also have fiber optic ports for long-distance transmission or anti-interference scenarios, such as connecting long-distance devices in power systems. Ordinary routers are mainly Ethernet ports used to connect common Ethernet devices.
Reliability and redundancy design: Industrial switches have redundant power modules to ensure uninterrupted industrial production. When one power supply fails, the other can continue to supply power; There is also a link redundancy function, which allows data to automatically switch to the backup link when one link is interrupted. Ordinary routers generally do not have redundant designs and have lower costs. On the factory automation production line, if the network interruption may cause production to stagnate, the redundant design of industrial switches can ensure the continuous operation of the network.
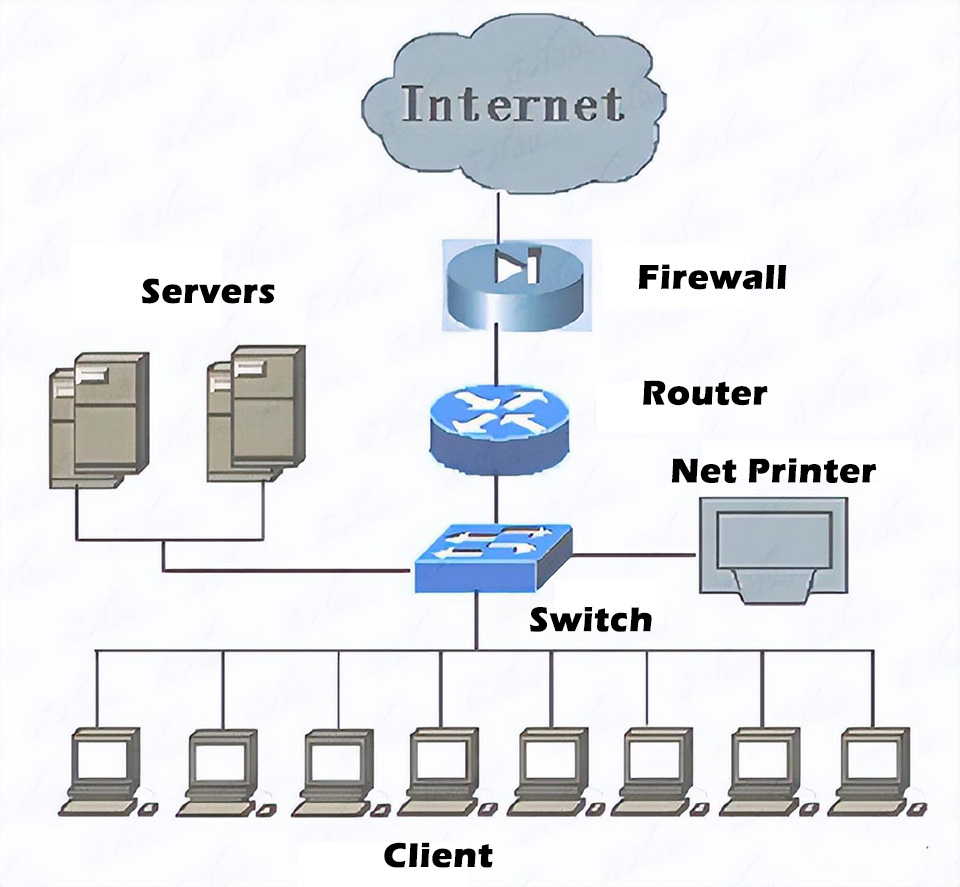
2、 Key points to note when using mixed applications
(1) Port speed matching
The port speed for connecting industrial switches and regular routers should be consistent. For example, if the port speed of an industrial switch is 1000Mbps, the corresponding connection port of a regular router should also be 1000Mbps. If the speed does not match, such as industrial switches with gigabit ports and ordinary routers with 100Mbps ports, data transmission will proceed at 100Mbps, causing network bottlenecks and affecting overall network performance. For example, when connecting the production workshop equipment monitoring system in the factory office, if the port speed of the workshop industrial switch and the office ordinary router does not match, there will be a delay in viewing the real-time data of the equipment.
(2) VLAN settings
If the industrial network is divided into VLANs (Virtual Local Area Networks), ordinary routers should be able to support the corresponding VLAN functions and settings. For example, industrial networks divide different production line equipment into different subnets through VLANs. Ordinary routers need to correctly set VLAN related parameters in order to achieve data interoperability between different VLANs. If set incorrectly, different VLAN devices may not be able to communicate. For example, production equipment in different areas of the factory is divided into different VLANs. When connecting these industrial switches to ordinary routers in the office, VLANs need to be configured correctly in order for office personnel to access the corresponding production equipment data.
(3) Network protocol support
Ensure that both industrial switches and regular routers support the required network protocols. Industrial environments often use industrial protocols such as Modbus TCP and PROFINET. If ordinary routers do not support them, they cannot communicate normally with industrial switches. For example, in a smart factory, communication between devices uses the PROFINET protocol. If a regular router does not support this protocol, it cannot access the industrial network. Common network protocols such as the TCP/IP protocol family are supported by both, but protocols specific to industrial environments require special attention.
(4) IP address planning
In a hybrid network, it is necessary to plan IP addresses uniformly. Industrial equipment, industrial switches, regular routers, and other connected devices must not have conflicting IP addresses. For example, the original IP address range for industrial networks is 192.168.1.0/24. When a regular router is connected, its LAN port IP address cannot be within this network segment, otherwise it will cause IP address conflicts and prevent devices from communicating properly. You can set the LAN port IP of a regular router to another network segment, such as 192.168.2.1, and then use the router's routing function to achieve communication between the two network segments.
(5) Security
Industrial networks involve important information such as production safety, and safety is crucial. Ordinary routers may have weaker security functions, so when connecting to industrial networks, it is necessary to strengthen security protection. For example, enabling router firewall functionality, setting access control lists (ACLs), and restricting external unauthorized devices from accessing industrial networks. At the same time, the management account passwords for industrial switches and ordinary routers should be set to be complex and regularly changed to prevent them from being cracked. In some industrial networks involving critical production data, if the security protection of ordinary routers is not in place, it may lead to data leakage or network attacks, affecting production.
3、 Negligible factors
(1) Appearance design
Industrial switches are designed to be sturdy and durable in order to adapt to industrial environments. They may have larger volumes and stronger materials. Ordinary routers have diverse appearances and place greater emphasis on aesthetics and compatibility with home and office spaces. In hybrid applications, appearance has no impact on network functionality and compatibility, and can be ignored.
(2) Brand differentiation
Industrial switches and ordinary routers from different brands are generally compatible as long as they meet the key conditions of port speed matching and protocol support mentioned above. The brand itself will not directly affect the compatibility of the two mixed applications, so there is no need to overly worry about whether the brand is consistent. For example, Huawei's industrial switches and TP-LINK's regular routers can be connected and used normally if their parameters and functions match.
When mixing industrial switches with ordinary routers, pay attention to the above key points and ignore irrelevant factors to build a stable, efficient, and secure network environment that meets the network needs of specific scenarios.
